What makes successful businesses stand out?
The secret sauce is understanding customers. Businesses that understand customers can make up to 60% more profit than their competitors.
And you know how they do it? Through customer feedback.
An exceptional customer feedback tool helps you gather, analyze, and turn this feedback into a roadmap for success. It’s not just helpful; it’s a game-changer.
Yet, as we explore the significance of each customer interaction, a crucial metric comes into focus – Customer Lifetime Value (CLV).
What’s CLV, and how can you measure and use it to grow your business? Let’s dive into these insights right here.
What is Customer Lifetime Value?
Did you know returning loyal customers spend an average of 33% more per order than others?
That’s the power of customer loyalty!
But how do we know which customers are really happy and they’ll keep coming for more? That’s where CLV comes in.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV), sometimes referred to as LTV (Lifetime Value), is a crucial metric in business that represents the total revenue a business can reasonably expect to earn from a single customer throughout its entire relationship. It takes into account the customer’s purchases, engagement, and interactions with the business over an extended period.
For instance, let’s say you love ordering pizzas from Domino’s, think about how much money you spend there in a year, two years, or even longer. CLV is like adding up all those pizza bills to see how much you’re worth to Domino’s.
For a business, CLV is important because it helps them see the big picture. It’s not just about one purchase; it’s about all the purchases a customer makes over time. This magic number tells businesses how much money they can expect to make from each customer in the long run.
Why CLV Matters?
89% of marketers believe that Customer Lifetime Value and excellent customer experiences are key to building brand loyalty. You see, in the fast-paced business world, CLV has emerged as a strategic superhero, influencing how companies approach their long-term success.
Here’s why CLV is crucial:
1. Long-Term Vision
CLV encourages a marathon mindset instead of a sprint towards quick wins where the focus is solely on immediate gains and not on cultivating a long-term relationship. It shifts the focus from short-term gains to a sustained approach, considering the entire customer journey over time.
2. Smart Spending
Companies often spend money on acquiring new customers without understanding their long-term value. Here, CLV acts as a financial advisor. It guides companies to invest their resources where it matters most—in activities that enhance customer loyalty and encourage repeat business.
3. Customer Happiness
CLV shifts the focus to customer satisfaction. By understanding the lifetime value of customers, businesses are motivated to prioritize customer happiness, knowing that a satisfied customer is likely to remain loyal and contribute to long-term revenue.
For instance, The regular Netflix user usually stays for around 25 months. Netflix says each customer is worth about $291.25 over time. They found out that some people leave because they don’t like waiting for movies in the mail. So, Netflix made a way to watch movies online to keep people entertained while waiting. By keeping an eye on these numbers and what users do, Netflix lowered the churn rate to just 4%.
4. Adapting to Change
Businesses might change strategies without considering the potential long-term impacts.
But, CLV serves as a strategic advisor. It helps companies make informed decisions, ensuring that changes in strategy align to maximize customer value over time.
5. Survival in a Competitive World
CLV transforms the race into a strategic competition. It’s not just about acquiring customers; it’s about acquiring and retaining valuable customers. This shift in focus is essential for sustained growth and survival in a competitive marketplace.
In essence, CLV is not merely a numerical metric; it’s a comprehensive guide that empowers businesses to navigate the complexities of the business landscape with a focus on long-term prosperity. It has become the secret ingredient for success, offering a strategic advantage in an ever-evolving business environment.
Calculating CLV: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
76% of businesses believe tracking customer lifetime value is important. But how to do that?
This step-by-step guide, tailored for businesses of all sizes, breaks down the process:
- Define the Time Period: Start by selecting a specific time frame for analysis, whether it’s a year, two years, or more. This period will be the focus for tracking a customer’s interactions with your business.
- Calculate Average Purchase Value: Determine the average amount a customer spends per transaction within the chosen time frame. Add up the total revenue and divide it by the number of transactions to find this value.
- Determine Purchase Frequency: Understand how often, on average, a customer purchases within the specified time frame. This insight provides a clear picture of customer buying behavior.
- Calculate Customer Value: Multiply the average purchase value by the purchase frequency. This yields the average value of a customer during the chosen period.
- Calculate Average Customer Lifespan: Identify the average duration a customer remains engaged with your business—this is their lifespan as a customer.
- Compute CLV: Multiply the average customer value by the average customer lifespan. The outcome represents the Customer’s Lifetime Value.
Let’s learn how to calculate the customer’s lifetime value.
Customer’s Lifetime Value Formula Breakdown:
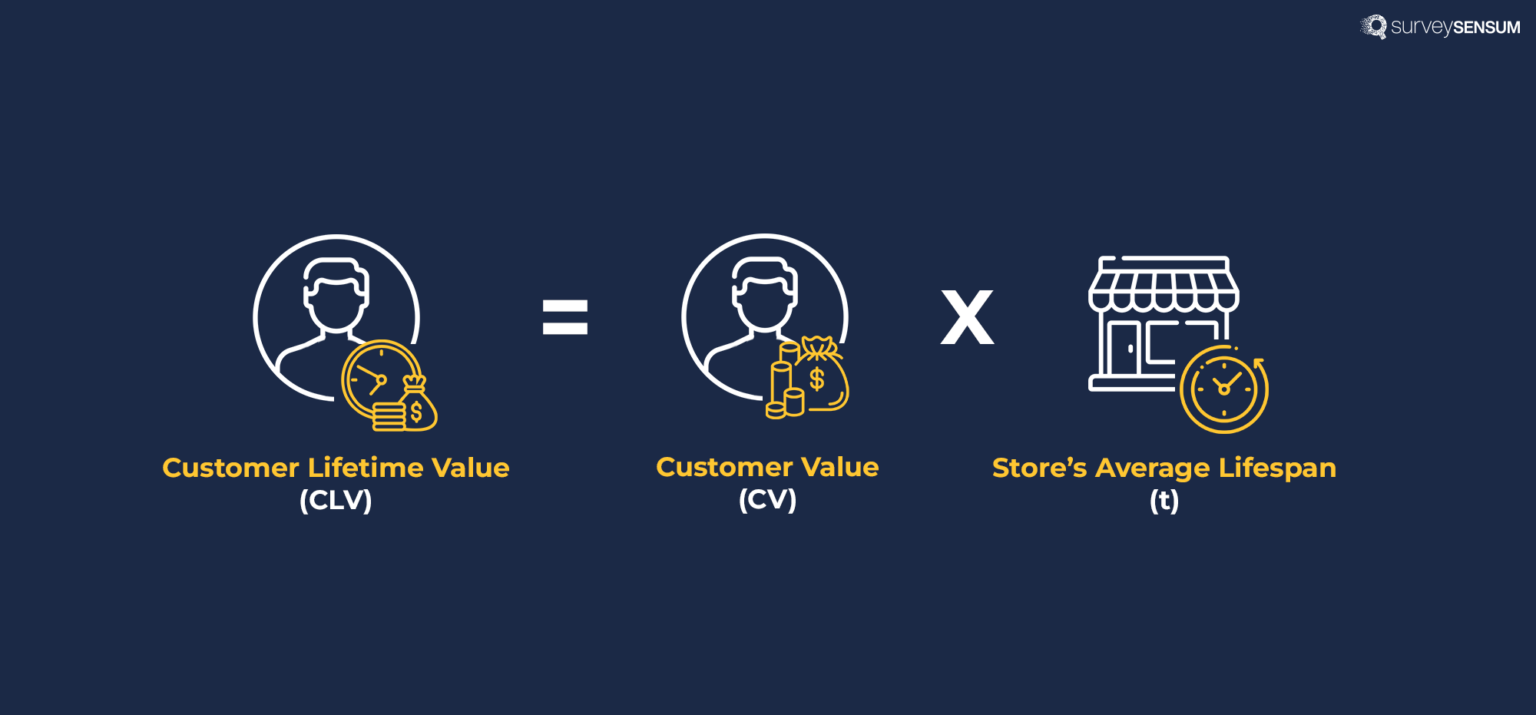
1. Define the Time Period:
Say, 1 Year
2. Calculate Average Purchase Value:
Total revenue is $50,000, with 500 transactions. Average purchase value = $50,000 / 500 = $100.
3. Determine Purchase Frequency:
Say your customers make an average of 3 purchases per year.
4. Calculate Customer Value:
Average customer value = $100 * 3 = $300.
5. Calculate Average Customer Lifespan:
Say your customers, on average, stay engaged for 2 years.
6. Compute CLV:
CLV = $300 * 2 = $600.
In this example, the Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is $600, indicating the average value a customer brings over two years.
In this example, the Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is $600, indicating the average value a customer brings over two years.
Calculate Your Customer Lifetime Value Now
-
- Average Purchase Value: Total revenue divided by the number of transactions.
- Purchase Frequency: How often, on average, a customer purchases in the chosen period.
- Average Customer Lifespan: The average duration a customer continues to make purchases.
The Impact of CLV on Business Decisions
Understanding the profound influence of CLV on business decisions involves exploring its impact on strategic planning, marketing endeavors, and the overarching landscape of decision-making within a company.
1. Strategic Planning
CLV acts as a guiding force in strategic planning by shifting the focus from short-term gains to long-term sustainability. It provides businesses with a valuable metric to assess the overall worth of each customer over time. This insight enables companies to make decisions that align with their long-term goals, fostering growth and resilience in a dynamic market.
2. Marketing Efforts
In the realm of lifecycle marketing, CLV plays a pivotal role. Armed with the knowledge of how much a customer is likely to spend over their entire engagement with the business, marketers can tailor their strategies for customer acquisition and retention. CLV data directs marketing investments toward activities that not only attract new customers but also ensure the satisfaction and loyalty of existing ones.
3. Overall Decision-Making
The influence of CLV extends across the spectrum of decision-making within a business. From product development to customer service initiatives, businesses armed with CLV insights can make informed choices that prioritize the long-term value of their customer relationships. This customer-centric culture approach resonates throughout the organization, fostering a culture that values and nurtures lasting connections with clients.
But that’s not enough! To build a profitable strategy, you need to clearly understand the difference between CAC and CLV. This will help you make the balanced use of both metrics.
Comparing Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) and CLV
| Metric | Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) | Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) |
| Definition | Cost to acquire a new customer | Value a customer brings over their entire engagement |
| Goal | To minimize and make it as efficient as possible | To maximize and ensure it exceeds CAC significantly |
| Balance Indicator | Ideally, CAC < CLV | Healthy when CLV significantly exceeds CAC |
| Impact on Profitability | High CAC relative to CLV can lead to financial strain | Balanced CAC and CLV contribute to sustained profitability |
| Consideration in Decision-Making | Critical for cost-effective customer acquisition | Integral for long-term business sustainability and growth |
In this section, we delve into the critical relationship between Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) and Customer Lifetime Value (CLV), emphasizing the significance of maintaining a delicate equilibrium between these two metrics for sustained profitability.
Understanding Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Customer Acquisition Cost represents the investment a business makes to acquire a new customer. It encompasses various expenses related to marketing, advertising, and other efforts aimed at bringing in fresh faces to the customer base.
Unveiling Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
On the other side of the equation, Customer Lifetime Value provides a glimpse into the long-term value a customer brings to a business. It factors in the cumulative revenue generated by a customer over their entire engagement with the company.
CAC vs CLV
The crux of this comparison lies in finding a harmonious balance between CAC and CLV. Ideally, the cost of acquiring a customer should be equal to the potential value that the customer brings over their lifetime. A scenario where CAC is significantly lower than CLV signifies a healthy and profitable customer acquisition strategy.
You must be wondering why is it so important to make a balance between these two metrics, right?
Importance of Balancing Metrics
- Profitability: Striking the right balance ensures profitability. If CAC is too high in relation to CLV, the business may struggle to recoup its initial investment, leading to financial strain.
- Sustainable Growth: A well-calibrated balance supports sustainable growth. By optimizing customer acquisition costs relative to the expected lifetime value, businesses can grow their customer base while maintaining financial viability.
- Informed Decision-Making: Understanding the interplay between CAC and CLV equips businesses with the insights needed for informed decision-making. It guides resource allocation, helping companies allocate budgets effectively to maximize returns.
Now that you are aware of the difference between CLV and CAC, let’s uncover how you can maximize CLV with the help of proper segmentation.
Customer Segmentation: Maximizing CLV through Targeted Strategies
Using customer segmentation can help businesses increase revenue by 10% to 15% and boost conversion rates by up to 50%.
These stats clearly indicate how customer segmentation helps businesses to make the most of their customers’ value over time. This strategy will help you with the same!
It involves dividing customers into groups based on similarities like age, buying habits, or preferences. By doing this, businesses can create special plans for each group, making their approaches more personalized and effective.
Here’s how it works:
- Understanding Different Customer Groups: Businesses figure out the different types of customers they have by looking at key categories like age, what they buy, and how they like to shop. Next, make customer personas that represent each segment of customers based on their characteristics.
Let’s take an example of a traveler’s customer persona created by a hotel booking site.

- Customizing Plans for Each Group: Once they know the groups, businesses create special plans for each one. This might mean personalized ads, specific products, or unique deals.
- Making Things More Personal: Customer segmentation allows for a more personal touch. Businesses can now meet the specific needs of each group, making customers feel more connected and likely to keep coming back.
- Using Resources Wisely: With targeted plans, businesses spend their time and money where it matters most. Instead of using the same approach for everyone, they focus on what works best for each group.
- Keeping Customers Around: Tailoring plans to different groups helps businesses keep customers for longer. By meeting the unique needs of each group, businesses build stronger, lasting relationships.
- Checking and Tweaking: Businesses regularly look at the data from customer segmentation to see how well their plans are working. If something isn’t quite right, they can make changes to keep things on track.
By understanding and treating different customer groups uniquely, businesses can not only make their customers happier but also get more value from them in the long run. It’s a smart strategy that helps businesses thrive in a competitive market.
Building Customer Loyalty: A Pillar of High CLV
In this section, we’ll delve into the dynamic interplay between customer loyalty and CLV. The heading emphasizes the pivotal role of customer loyalty as a foundational element for achieving a high CLV.
1. Investigating the Symbiotic Relationship
Here, we aim to uncover the reciprocal connection between customer loyalty and CLV. It’s about understanding how these two elements depend on each other. Loyal customers contribute significantly to a high CLV, and a high CLV reflects the success of loyalty-building strategies. It’s a symbiotic relationship where each strengthens the other.
Starbucks is a great example of this, as it does a great job with its loyalty program!It’s not just about giving customers free coffee, but it also makes everything easier. Their loyalty program, Starbucks Rewards, lets customers order in advance and pay using their phone. That’s why Starbucks has lots of loyal customers who keep coming back!
3. Strategies for Nurturing Long-Lasting Customer Relationships
26% of people say that “trust” and “consistency” are super important when it comes to sticking with a brand.
Now, let’s talk about making customers loyal to your brand. You can create personalized experiences, launch loyalty programs, and provide seamless customer service. These are tools that help businesses build strong connections with customers. The big aim is to show that customer loyalty is important for your business. It’s like the foundation that helps businesses have a high CLV and keep it strong.
One of the best examples of this can be Adidas. Adidas excels in customer care by understanding, providing excellent service, and personalizing experiences. They listen to feedback, implement reward programs, and stay consistent in their brand. Known for innovation, in 2020, they launched sustainable products like “Prime Green,” made from ocean plastic, setting the trend for eco-friendly practices in the industry.

Avoiding Pitfalls: Common Misconceptions About CLV
There are some common misconceptions that businesses encounter. The importance of CLV is undeniable—it’s a metric that guides decisions on customer acquisition, retention, and overall business strategy. However, navigating CLV can be tricky if certain misconceptions persist. Let’s explore these pitfalls here:
1. CLV is Only for Large Businesses
CLV is beneficial for businesses of all sizes. Small and medium-sized enterprises can gain valuable insights into customer behavior, tailor strategies, and enhance long-term profitability.
2. CLV is Static
CLV is dynamic. It evolves as customer behavior, market conditions, and business strategies change. Recognizing this dynamism is crucial for accurate decision-making.
3. CLV is Too Complex to Calculate
While CLV involves multiple factors, various tools and simplified models are available to help businesses calculate it effectively. It’s an investment in understanding the future value of each customer.
4. CLV is Only for Customer Acquisition
CLV extends beyond acquisition. It aids in customer retention strategies, highlighting the importance of keeping existing customers satisfied for prolonged revenue streams.
5. CLV is a One-Size-Fits-All
CLV is the most effective when customized to the specifics of each business. Generic approaches may lead to inaccurate assessments of customer value and hinder strategic decision-making.
6. CLV is Exclusively Financial
While financial metrics are essential, CLV should also consider customer satisfaction, brand loyalty, and other non-monetary factors influencing long-term relationships.
By addressing these common misconceptions, you can avoid potential pitfalls associated with CLV.
Conclusion
In wrapping up our journey through Customer Lifetime Value, it’s clear that this metric is a game-changer for businesses. We’ve explored its role in understanding customer worth, optimizing costs, and crafting smart strategies.
Businesses gain powerful insights from balancing acquisition costs to embracing customer loyalty as a foundation for success. We’ve debunked misconceptions, ensuring a clearer path for decision-making.
CLV becomes a guiding star as businesses move ahead, steering them toward sustained success. It’s more than just a metric; it’s a compass pointing to a future where lasting customer relationships measure success.
By avoiding common pitfalls, embracing smart strategies, and understanding customer dynamics, businesses are set to navigate the market with wisdom. CLV isn’t just about transactions; it’s about the enduring value of happy and loyal customers, paving the way for a successful future.











